SEO Copywriting: The Basics
SEO is all about brand awareness and visibility. When your target audiences search for a particular product, service or topic that’s relevant to your business, you want them to find your website before that of your competitors. The best way to make this happen? Implement SEO best practices consistently throughout your content with strategic SEO copywriting.
SEO copywriting involves creating useful and well-crafted web copy that targets specific keywords your target audiences are using. The goal is for your content to rank higher in organic search engine queries, be ultra-relevant to your target audiences and drive more qualified traffic to your website. And while Google is constantly tweaking their search algorithm, the basic rules of SEO copywriting continue to apply.
Your SEO Copywriting Cheat Sheet
Whether you’re writing copy from scratch or updating copy that’s already published, use this invaluable cheat sheet to guide your SEO copywriting. The following SEO tactics and strategies will ensure your web team has everything they need to populate, publish and optimize your pages for organic search.
1. Keyword Research, Step-by-Step
- Identify Potential Keywords
To write effective SEO copy, you must first understand what you’re optimizing for. Start by identifying the search terms (i.e. “keywords) that you want your website to rank for. Put yourself in the shoes of your prospects/customers:
-
- What products/services/topics are they interested in?
- What type of language do they use to describe these things?
- What problems or challenges do they have?
- How do they describe what your business does?
- Use a Keyword Tool to Refine Your List
Input your list of terms and phrases from above into keyword tools like Yoast Google Suggest or Ubersuggest. This will help you understand which keywords are driving the most search volume and provide ideas for expanding and refining your initial keyword list.
2. On-Page Optimization
Once you’ve refined your keyword list, it’s time to integrate these keywords into your site’s content. SEO copywriting involves a page-by-page approach. Each page on your site should target a primary keyword, as well as several related (secondary) keywords.
Here is how to set up the basic SEO elements for each page.
- Focus keyword
- Use it in an H1, H2 or other subheading
- Ideal if it’s used in the URL for the page
- Use it in the first paragraph of copy
- Ideal if it’s used in the SEO title
- Use it in at least one image alt tag on the page
- Don’t choose the same focus keyword for every page
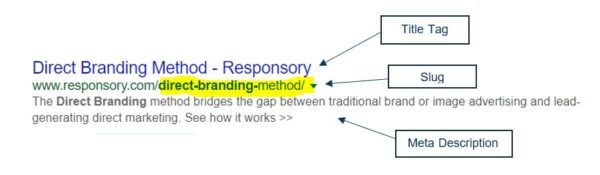
- Title tag
The title tag is the “headline” in organic search results. It’s one of the most impactful places you can put your page’s primary keyword.- Aim for 55-60 characters
- Typically, it’s automatically generated using this formula:
Primary Keyword – Secondary Keyword | Brand Name
- Slug:
The page slug is the end part of a URL that identifies a particular page on a website. It’s typically the editable part of the URL that explains the page’s content to users.- Contains the focus keyword/phrase
- Does not contain stop words (filter out any unnecessary words like “a,” “the” and “and”)
- Is short but descriptive
- Meta description:
The meta description provides an overview of what the page is about. It’s what users see when your page appears in organic search results. (Or what is automatically displayed when a user shares your page via a social post).- Put the most important words in the beginning
- Aim for 150-165 characters maximum
- Actionable, active voice
- Includes a call-to-action
- Accurately represents copy on page
- Contains the focus keyword/phrase
- Is unique to your site and is not repeated on any other page in your site
3. Organization & Critical Page Elements
Often referred to as “Information Architecture,” the way you organize your website and interlink between pages can impact how your site content ranks in response to searches.
For each page of your site, contemplate the critical elements listed below as they relate to your business, website goals and page design. You will need to tailor your SEO copywriting efforts for the specifications of your site’s primary, secondary and tertiary level pages.
Overall
- Purpose of page:
How does the page benefit your target audience? This is a useful reference for the writer, editor, proofer and people who are reviewing and approving copy. - Top 3 search terms:
These are words or phrases (keywords) your target audience would use to find this page when searching online (see “Keyword Research” below) - Sectiontitle:
This indicates where this page will live within the site’s organizational structure. If it is a primary page, it is at a parent level and this field would be the same as the navigation title. - Navigation title:
This is the name of the page that will show up in your navigation structure/site menu. The navigation title and the page title are often the same, but not always. - Page title:
This is not your page’s primary headline. It’s what you can see at the very top of your browser and is populated by your page’s source code.
Hero
- Hero image alt tag:
A hero image is a large image across the top of the page, below your navigation. If there’s copy on the hero (i.e. the navigation title of the page or a marketing message), make sure the copy is handled as text, which is searchable by search engine spiders. - Hero copy:
What should the copy on the hero image say? Hint: keep it short and to the point. - Hero call to action:
Is there action you want the user to take? If so, write it succinctly. Note if it is a text link and where this text link should take the user. - Hero call to action button copy:
Will there be a button for that action? If so, what will the button copy say (2-4 words) and where will it take the user?
Body
- (H1) Body copy headline:
This is typically the largest sized text on the page. It tells the user what the page is about and why it is important. - Body copy:
Minimum 350 words recommended. The bulk of the page’s content will be placed here. Think about your target audience’s hot buttons and what language they would use. Remember, you are writing for people AND search engines.- Paragraphs should be short and to the point.
- Use conversational tone and wording.
- Use business terms as necessary but avoid jargon.
- Use active voice in body copy, opposed to passive.
- Use a transition word or phrase in at least 30% of your sentences.
- Limit sections of copy (between headers/subheads) to 300 words to break up copy.
- Try to limit sentences to 300 words or less.
- (H2) Subheads work.
- Subheads break up blocks of copy and convey key points of information succinctly.
- Lists are great, too, because they:
- Use bullets that catch the eye
- Are easily scannable
- Organize key ideas
- Inset image alt tags:
Images, graphics, charts to further illustrate or “sell” your body copy messaging are useful in drawing in readers and keeping their eyes on the page longer. All images on the page require an alt tag. At least one of them should contain your focus keyword/phrase. - Outbound/external links:
Incorporate a text link in your copy that takes users to a page outside of your website (3rd party site). Consider having that link open in a new browser window, as a rule. - Internal links:
Cross promote additional information within your site by incorporating at least one text link in your copy that takes users to another page within your website.
Call to Action
- Call-to-actioncopy:
After visiting and engaging with your page content, what do you want the user to do next? Visit another page? Fill out a form? Download something? Click to purchase? Explain the next logical step in their journey and its benefit to them in a succinct manner using action-oriented copy. - Call to action button copy:
This is the very short copy to appear in the link or button to take action. - Button destination:
This is where the CTA button takes the user.
TIP: Keep Keyword Intent top-of-mind
“Keyword intent” refers to the reason people search for the keyword you’re targeting. To deliver the most relevant search results, search engines favor web content that most closely matches keyword intent. Think about what users are looking for to ensure your page content aligns with the keyword(s) you’re trying to target as closely as possible.
We hope you find this SEO copywriting cheat sheet helpful as you craft or revamp your website, microsite or landing page copy. You may also find “Is Bad Grammar Killing Your SEO?” insightful as well. If you find the whole process overwhelming or too time consuming, consider consulting with the digital marketing pros at Responsory. We’re here to help!